Car Lease Calculator
Car Lease Calculator
What does a car lease calculator do?
Lease calculators take the facts and figures you gather in your research and compute a lease payment according to multi-step formulas leasing companies use. These calculations are more complex than auto loans, which typically total sales price, taxes, and fees, subtract any down payments, rebates, and trade-in values, and then apply an interest rate over the loan term to arrive at a monthly payment. A lease calculator factors in all of that, plus the residual value of the car and the money factor (or interest rate) on the adjusted capitalized cost.
How does a car lease work?
The financing entity retains vehicle ownership during the agreement term in a car lease. This ownership status is the significant difference between leasing and financing a car with an auto loan. During your auto loan, your payment goes toward reducing your total debt and increasing your equity. After making your final payment at the end of the loan term, you get a clear title to the car - you own it. In a lease, you have the right to use the car while you make payments, but at the end of the lease term - the financing entity still owns the vehicle. You have no equity. You may buy the car from the financing entity at that point, usually by paying the residual value. But you'll have to pay a fair sum and maybe even take out a fresh auto loan.
Why choose leasing over financing?
Many shoppers are attracted to leasing because the initial outlay on a lease is often substantially lower than the down payment on a loan for the same vehicle and will frequently carry a lower monthly payment. Some shoppers care more about having a newer vehicle to drive than having equity in a used car, so they move from leased vehicle to leased vehicle through the years. Some business owners discover tax advantages to leasing, particularly for vehicles used primarily for work. Consult your accountant or financial adviser to determine the implications of leasing over financing in your financial situation. Curious about owning vs. leasing costs? Go to our cost to own page or check out our depreciation calculator to see how a car's value will change over time.
For more information, see our Car Leasing Guide.
Financing Tips: Leasing
Should you lease or buy an electric car? We’ve got answers in the wake of fluctuating interest rates and federal tax credits for EVs.
Get to know about used car leasing, mileage restrictions, if it’s a good idea, and more.
Explore car leasing with our guide covering pros and cons versus buying, negotiating costs like money factor, mileage caps, key terms, and responsibilities.
FAQs
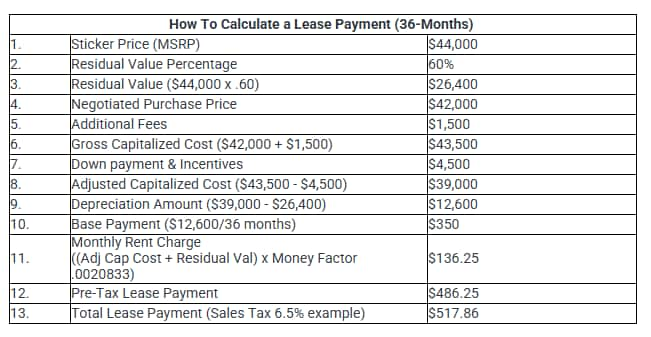
Many variables go into calculating lease payments. Look for a vehicle with a high residual value and lease terms with a low money factor for the most value. You can gauge how good a lease deal is with a quick rule-of-thumb calculation: Divide the monthly lease payment by the car's MSRP. It's a better deal if the result is less than or close to 1%, and not as good the higher the result is above 1%.
Your budget, needs, priorities, and lifestyle are unlike anyone else's. However, spending 20% of your take-home pay for a car and related costs (monthly payment, auto insurance, gas, maintenance, etc.) is a widely accepted rule of thumb. No matter how long it takes to save up the money needed for upfront leasing costs such as down payment, taxes, registration fees, and so forth, ensure you have enough income for your monthly budget to cover your current financial obligations in addition to new transportation costs.
An auto lease has a "money factor" to cover the financing, which is similar to a car loan's interest rate. Lease documentation displays the lease money factor (or "lease factor" or "rent fee") as a four- or six-digit decimal instead of the percentage seen with a loan's annual percentage rate (APR). To convert a lease money factor to a more familiar interest rate percentage, multiply it by 2400. For example, a .002083 money factor is equivalent to a 5% APR; a .0025 money factor equals 6% APR.
A car's residual value is the estimated value of the vehicle at the lease end. The financial institution or bank calculates the residual value as a percentage of the car's MSRP. A car with a high residual value will have a lower monthly payment than a similar-priced vehicle with a low residual value. The best residual value will be 65% or higher. Cars that don't hold their value as much might have a 55% residual value. As a result, even if they have the same sticker price, the vehicle with a lower residual value will cost more to lease than the model with a high residual value.
